Diaper Rash Bleeding: How to Soothe, Prevent, and Heal Your Baby's Sensitive Skin


Essential questions about diaper rash bleeding addressed in the article:
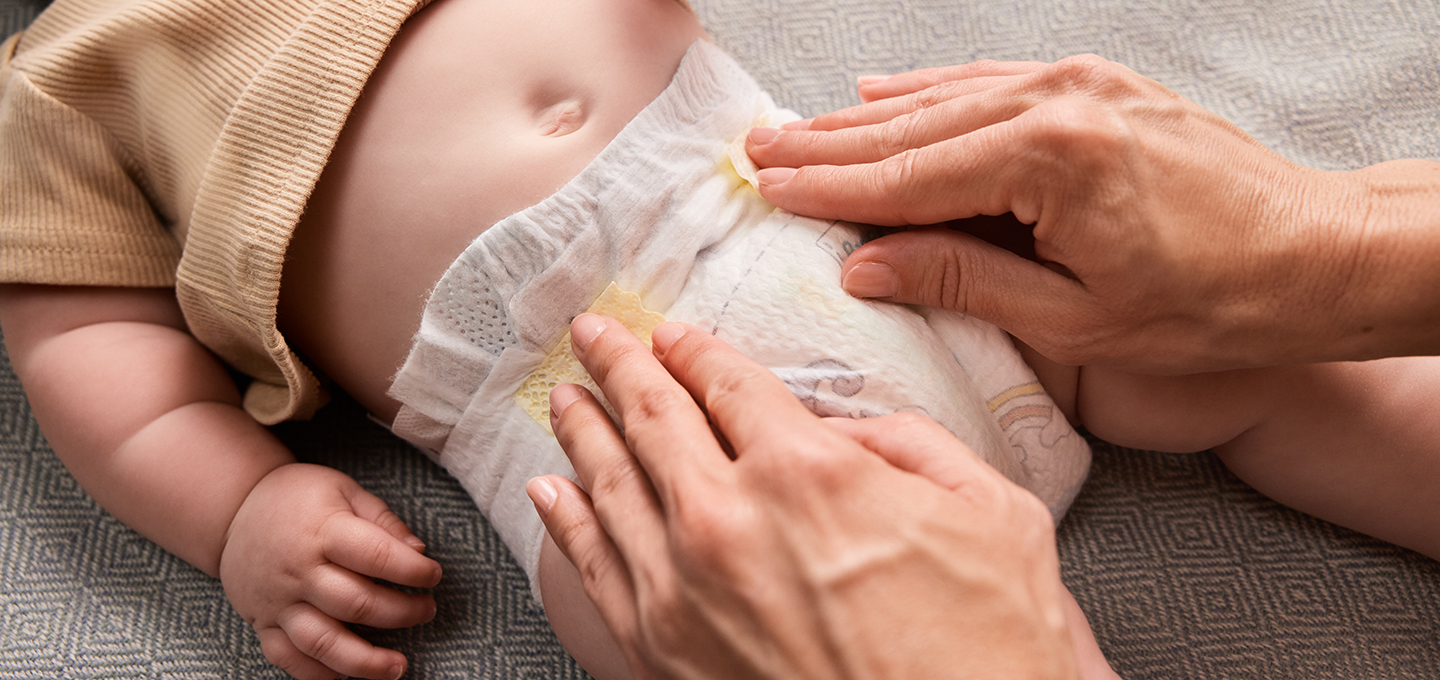
Diaper rash is a common concern for many parents, but when you notice that your baby's diaper rash is bleeding, it can be particularly alarming. Diaper rash bleeding might seem severe, but understanding what’s happening and how to manage it may help you care for your little one's sensitive skin. In this article, we'll explore the causes, treatment options, and when it’s important to seek help from your baby’s healthcare provider.
Can a Diaper Rash Cause Bleeding?
A diaper rash is a common skin irritation that affects babies, usually appearing as red, inflamed areas on the skin in the diaper region. It can be caused by prolonged exposure to wetness, friction from diapers, yeast or bacterial infections, an allergic reaction, or sensitivity to certain products used on the skin.
If it becomes severe or is left untreated a diaper rash may cause bleeding. Severe diaper rash bleeding often occurs when the skin becomes so irritated and inflamed that it breaks down, leading to small cuts or sores that may bleed. The constant friction from diapers, combined with exposure to urine and stool, may exacerbate the condition, making it more painful and difficult for your little one.
It’s important to address diaper rash promptly to prevent it from worsening to the point of bleeding. Keeping the area clean and dry, changing diapers frequently, and using a barrier cream are essential steps in managing and preventing diaper rash.
Keeping the area clean and dry, changing diapers frequently, and using a barrier cream are essential steps in managing and preventing any diaper rash blood from occurring.
Causes of Bleeding Diaper Rash
Diaper rash bleeding develops due to several factors, often related to prolonged irritation or infection. Here are some common causes:
Understanding these causes may help prevent and manage diaper rash before it becomes severe enough to bleed.
How to Treat a Bleeding Diaper Rash
When you notice a bloody diaper rash on your little one, it’s essential to take immediate action by contacting your baby’s healthcare provider as soon as possible. Bleeding may be a sign of a severe rash or infection that may require professional treatment. However, while you’re waiting to see the healthcare provider, you may take the following steps to help soothe your little one’s skin:
Diaper Rash Bleeding Remedies
While diaper rash home remedies may be effective for treating mild cases, it's important to exercise caution when the rash has progressed to bleeding. When you notice diaper rash bleeding, it’s best not to rely solely on home remedies. Instead, contact your baby’s healthcare provider to ensure proper treatment and avoid potential complications. When it comes to your little one's health, it's always a good idea to stay on the safe side.
When to Contact a Healthcare Provider
If you notice that your baby’s diaper rash is bleeding, it's important to contact their healthcare provider as soon as possible. Bleeding may be a sign of a severe rash or a potential infection that needs professional medical evaluation and treatment. It’s not recommended to rely on diaper rash home remedies alone when bleeding is present, as this could lead to complications.
Additionally, if the rash doesn’t improve within a few days, spreads beyond the diaper area, or is accompanied by other symptoms like fever or pus-filled sores, these are all signs that you should seek medical advice immediately.
Your little one’s healthcare provider may assess the severity of the rash and recommend the best course of action, which may include prescription treatments or other medical interventions to ensure your baby’s skin heals quickly and comfortably.
The Bottom Line
In summary, while diaper rash bleeding can be alarming, it’s important to seek guidance from your baby’s healthcare provider to ensure proper treatment. Addressing the rash early and following medical advice may help prevent further complications and keep your baby comfortable.
For parents looking for additional support, the Pampers Rewards app offers discounts and digital offers that can help you save on the Pampers products you need to keep your baby happy and healthy.
Read more about Baby
Join a World of Support
through Pregnancy and Parenthood.
TRACK WITH TOOLS
LEARN WITH EXPERTS
GET REWARDED